Since the Industrial Revolution and the advent of manufacturing, business automation has progressed in leaps and bounds across every industry, task, and function. From mechanisms and button controls replacing manual labor to forms for document filling and telephone communication, all these advancements have served progress.
In 2016, the concept of automation took on a different meaning than it did 100 years ago. Globalization and virtual platforms, accessible even from mobile devices, transformed “production mechanization” into “digital enterprise management.”
What is a Business Process and its Essence?
A business process is the algorithm of actions a company takes to provide a product to a customer. This algorithm is repeatable and ensures growth and profit. Other cycles not directly related to the customer but saving costs or increasing profit are also business processes.
The quality of execution depends on the simplicity of the tasks set and their proper regulation. Regularly updating, supplementing, or reducing the sequence of actions affects the company’s market competitiveness.
An Illustrative Example of a Business Process: Car Rental
To rent out cars like Skoda, Volkswagen, or Mercedes, you need to:
- Buy a used car, open a bank account, and set up a sole proprietorship (starting capital).
- Perform maintenance and refuel (resource provision).
- Place an advertisement (marketing, advertising).
- Meet the client, sign a contract, and make the payment (realization).
- Hand over the keys and power of attorney for the car, agree on the return method (delivery and product support).
- Collect the car, keys, and close the contract on the agreed date (end session).
Steps 3 – 6 form the cyclic algorithm that generates profit.
More Complex Business Processes
Business processes can be categorized as:
- Core: Deliver results to customers, such as extracting, processing, and packaging oil for an oil company.
- Support: Distribute resources and supplies, such as materials, labor, and equipment repair for an industrial electronics factory.
- Management: Control specific aspects, such as sales oversight, logistics problem-solving, and developing a 5‑year growth strategy.
Advantages of Adopting Business Process Management (BPM)
Transitioning from traditional departmental divisions to BPM can be costly in terms of man-hours and often requires a business consultant. However, the benefits include systematically reducing costs and increasing revenue. Additionally, a company can achieve ISO 9001 quality certification, affirming its readiness for European and American markets.Practical Implementation
Automating business processes is beneficial in various sectors:
- Industrial Enterprises: Orders, material procurement, production, packaging, delivery, and reporting.
- Hazardous Industries and Extraction: Robotics and conveyor system improvements, environmental pollution control, and resource consumption monitoring.
- IT Companies: Task management among programmers, testers, and salespeople, technical support, bug tracking, and 24⁄7 online resources.
- Service Companies: Individual services and phone consultations requiring CRM systems, document flow management.
- Banking: Client database maintenance, unbiased loan decision mechanisms, online banking, and fraud prevention.
- Analytical, Legal, and Research Centers: Monitoring and analyzing large, regularly updated databases, statistics, and disaster prevention.
What Should Not Be Automated?
- Customer Problem-Solving Interface: Automated booking systems are excellent, but complex phone trees can frustrate customers.
- Final Decision-Making: Systems can be hacked; overturning a critical decision isn’t always possible.
- Translation: A native speaker outperforms automated translation tools.
- Emergency Response: Data collection can be automated, but human intervention is crucial in emergencies.
How to Write a Business Process Properly
First, document the current process, create an ideal process map, and then find the shortest path between reality and the ideal, focusing on cost reduction and profit increase. If the structure is complex, something in the company needs fixing.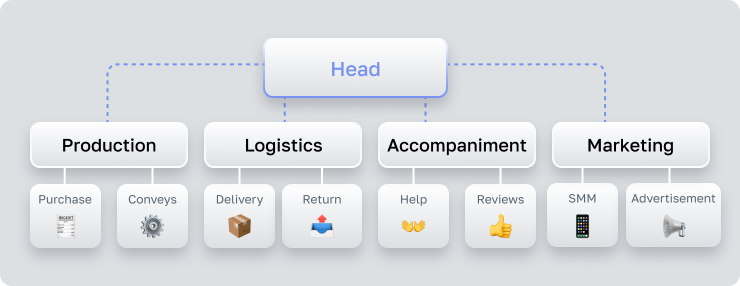
Use flowcharts, known as maps, to visualize core, support, and management processes. Columns represent participants, and rows indicate time intervals and actions.
Steps for Implementing Business Process Automation
- Identify Processes for Automation: Determine which processes can be automated, such as task transfers, procurement, and logistics.
- Unified Database: Centralize data and ensure individual access levels.
- Data Entry Templates: Standardize forms for data input.
- Built-in Calculation Formulas: Automate tax, VAT, and reporting calculations.
- Notifications and Reminders: Use mass and segmented mailing, reminders within the admin panel or on smartphones for quick response.
Popular Types of Automation
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Comprehensive business automation with virtual infrastructure.
- Public Offer or Digital Contract: Eliminates the need for faxing signed documents, offering 24⁄7 access and history.
- Apps for Finance, Analytics, and Management: Tools for customer interaction, weekly newsletters, and notifications.
Conclusion
Since 2016, company leaders recognize that process automation is a necessity. Advanced technologies, consultants, and common sense help implement process management and commerce at a new level. Applications and programs for simulating business process automation are available to refine algorithms and ensure smooth operations.By automating beneficial actions, companies can significantly improve efficiency and productivity.