This question is asked by entrepreneurs of the industrial sector involved in the production of material goods; however, the answer to this question will also be useful to customer service sector, IT, and social projects.
Lean Management (also called «lean manufacturing»), as well as Kaizen philosophy and other management tools that can be applied in every business and process. Saying «every» before «business and process» is not an exaggeration because you can optimize everything. It is a way of thinking and productive action and not just a tactic based on a couple of algorithms.
Lean production is
There is an abundance of synonyms: Lean manufacturing, lean management, lean thinking ... even lean transformation. Thinking and transformation (the word «transformation» itself can be used as a synonym for the lean methodology) as a philosophy and theory of doing business, production and management — as a practice.
The words also reflect the idea of just-in-time production, introduced into the Toyota as the first ever sample of the lean method and the continuous improvement of the conveyor production of cars. Tiffany Ono is a lean principles the development engineer after the Second World War.
Its postulates:
- Waste elimination,
- Enhancing workers’ rights and capabilities,
- Stocks decrease,
- Productivity increase.
While Henry Ford supported resources for the «ahead of the demand approach on his production line, Toyota worked on building partnerships with suppliers and in fact made cars to order.
Many industrial start-ups already begin with the transformation, applying the methods and tools from the start of production and up to the last stage of customer support. Many years of business can also be restructured from the old «regime» to a new way of thinking, although this requires persistence and patience from managers. This path is more profitable in the long run.
It’s amazing how the lean manufacturing system changes the hierarchy in the company structure. Instead of managers and staff, a community of multi-disciplinary employees is formed. All the company’s resources, including people, are applied to the fullest: Everyone can offer improvement, everyone can test their idea in practice, and everyone is responsible for the complex result. This flexibility allows you to make changes instantly, and therefore respond to customer requests, competitors’ attacks and market unrest.
What is Lean management
To put it simply, Lean or lean manufacturing is a project management methodology in a company that eliminates all interference with manufacturing. Time and resource waste negatively affect the result. If the process can be done faster, better, and cheaper — it is worth doing right away.
Work algorithms revision constitutes of two stages:
- Analysis. In order to understand whether the current order in the company works well, you need to analyze all the processes and make a diagram. Call center scripts, order acceptance algorithm, logistics, work with returns in the online store; technical support scripts, processing applications in the bugtracker, rolling out updates in the grocery IT company. Register the whole procedure, determine the bad places yourself or apply the programs (any software for visualizing algorithms, bottlenecks, resources, and time).
- Making changes. Having found «vulnerabilities»: Job coordination problems, lack of resources, or outdated bureaucratic processes, suggest an alternative. The alternative does not have to be an innovation or include dramatic changes and the ideal solution. It can be just a way to do better. You can go through the options proposed by the team; however, not only discuss them but implement them in practice. No one knows in advance what will be useful in your particular project. The benefits and costs of each alternative are revised based on the results of the practice. The best option is implemented for good.
Both stages are recurring. Lean manufucaturing is never complete. It is a constant improvement of details. Lean does not provide grand innovations, but it does offer continuous improvement in small steps.
For the CEO
The main task of the manager is the profitability of the company. One way to achieve it will be to solve problems and reduce production costs, and another one — will be to focus on creating «value» for the client in a product or service. The most interesting thing is that by correctly determining the value for the client, you can direct the strength of the team and material resources only to what is important and reduce the cost of the unimportant.
In other words, Lean helps to save without losing quality and ultimately eliminating useless processes from the company’s algorithm.
For example, a client needs a woodworking machine.
- What is really important for the buyer? Price, functionality and delivery are important to all but there are price-oriented clients out there (low-cost machine models are cheaper) and quality-oriented (machines that allow to make complex and exclusive projects with thread). They all want to get the machine into the workshop quickly and accurately.
- What can be optimized or improved? Raising quality to raise the price is justified. Choosing licensed products with certification in a language known to the consumer, you can conduct a briefing. Providing delivery using a reliable logistics agency, with which the favorable conditions for cooperation had been established.
- What to remove? Remove all actions that interfere with the work. There is a train coach repair plant with geographically distributed workshops. Every day, its managers gather in the main building for a meeting to agree on a list of projects. If you implement a unified case management system, you can get rid of daily time loss from planning meetings, which is 7 hours of each shop manager per week.
- What needs to be done and in which order to win loyal clients? From the clients’ perspective, the purchase algorithm looks like this: First, accurately determine the model of the machine, then the method and address of delivery. It will not make sense to the client to be asked to log in and enter the address before choosing a product. If the request to fill out the address goes after the online consultant in the pop-up window helped to choose a model, configuration and other nuances — the client then feels trust and is satisfied. Consumer value is met, and tasks are performed on time. There is also an algorithm on the part of the company — you cannot send an order until it is paid. It is honest and eliminates the problems with the deceived expectations of both parties.
The goal of the director in Lean methodology is to bring the process of production, sale, and delivery of goods to the client to its idealized perfection. In this case, however, the focus is to benefit the client and not the company. The company’s profit becomes a concomitant success, thanks to the saving of time and resources in the production and growth of profits.
For personnel
What is the basis of lean production for employees of a plant or IT support center of a company? Properly applied methodology saves raw materials, improves working conditions, and helps workers earn more.
Lean should also be properly implemented into the company. If you use the method without giving it too much thought, the person in charge can:
- buy low-quality components in order to save
- rearrange the equipment in the workshop to reduce the distance between the conveyors but forget about the length of the power supply cables
- register a calendar of experiments and prohibit unplanned creativity
- to launch penalties for working tools brakage but not check their quality and condition
- Add your version.
The Lean methodology welcomes constant ideas exchange among the employees.
If the methodology is adopted in a team, then any plant worker can offer the director their idea of improving the workflow. The reason behind that is because an employee who directly performs the work process sees much better where and what can be improved in this process. With the constant introduction of such proposals, the plant certainly increases its efficiency.
At the same time, the worker will be rewarded if the idea turns out to be useful. He or she will receive a blank check on the implementation and practical tests of the ideas. Only through trial and error can you find the right path and lean manufacturing recommends trying and improving constantly.
For example, a convenient mobile organizer will reduce the number of missed deadlines and increase the speed of the marketing and design departments table. Implementing it in a company will be time-saving, which means it will be the basis of lean manufacturing.
For the company
Both the head of the company and the ordinary executor project create the value of the product for the client with their actions. And all their efforts are directed at achieving this.
The benefit for the client arises not in certain moments, like choosing a product, accepting an order, packing it in a warehouse, or delivery date.
Value is created by a stream of result-oriented processes:
- Online consultant helps to choose the size, model, and color;
- Placing an order, you can choose the method of payment via credit card or cash to the courier;
- It includes warranty, replacement or return coupon, gift cards, or invitations to a thematic event;
- You can set up the date and time of delivery, call the courier, or select a specific network store for self-pickup.
The non-linear work of the whole company allows to simplify the flows, change their algorithms so as to gain savings, increase the value at the same cost, or significantly reduce the percentage of scrap and returns.
In addition to pure value and the absence of defective copies, customer customization of the product is important, especially in the consumer segment. If a company can rebuild its conveyor belt without significant losses, produce different or new product models, then it will definitely win in the competition. Even making prefabricated individual kits from basic parts or providing exclusive sets to order is already a tangible advantage in the market.
Muda, Mura, Muri
This is how you call waste and unnecessary expenses in the Lean methodology. In other words, anything extra that is worth removing. Anything that does not add value to the customer. Muda (waste), Mura (unevenness), Muri (overburden) — words from Japanese my account customer that got accustomed in English business slang.
Muda- waste, unnecessary expenses. Management mistakes consequences.
| Muda | In Industry | In IT |
| 1. Transport | Miscalculation of logistics, unnecessary movement of raw materials, goods, documents or data. | Useless transfer of information between databases and departments table. Unnecessary tools or constant document switching. |
| 2. Inventory | Excessive stocks of raw materials, semi-finished and finished products. | Projects that are stuck in the «under development» stage. Bugtracker clogged with obsolete queries. Cumulative backlog of orders. |
| 3. Movement | Unnecessary movement of people around the workshop, offices, between the warehouse and the director’s office. | Fragmented databases, bad search navigation. Physically distant local media. The need to travel often to meetings. Many tabs in browsers, many messengers, or other ways to decentralize data and communication |
| 4. Expectations | Simple people and equipment. Waiting for instructions, verification, access to information. Lack of tools and equipment for the smooth operation of staff. | The absence of all the equipment for work, especially among software testers. Problems with access to the database, interruptions of the Internet, electricity and other causes of programr downtime. |
| 5. Exorbitant development | Excess stage in processing, waste of raw | After the request «a sketch, preliminary data, approximate indicators», it will be an error to make a complete code, in-depth analysis or development plan in accordance with the growth / decline of indicators |
| 6. Overproduction | Unjustified production of the product prior to ordering or in bulk. The product is obsolete before the sale stage. | In the finished project, there is an unsolicited amateur, incorrect binding to the past events or technologies. |
| 7. Defects, waste | The product does not comply with standards, order or company regulations. | Mismatch of requirement specifications. Additional iterations of edits. |
| 8. Potential* | Ignoring the potential and skills of colleagues. Unfair exploitation of labor, banning the initiative of workers. | Lack of career growth. Indifference to workflow optimization suggestions. |
| 9. Resources* | Lack of economic. Equipment, lights and other technical resources should be turned off when work stops for the night, at the end of the production). | Log out, turn off the PC before leaving. Control the operation of air conditioning, heating, printer, kettle and microwave (at least). |
| 10. By-products* | In addition to the final product, products accompanying the creation process can be produced. Additional parts from metal scraps at the factory of pipes, repair services at the station for sale of used cars | Certain functions of the software can be an independent product. Developing an application with the search for the nearest cafe can lead to two more possibilities: Profit on advertising for restaurants, profit on advertising events. |
* Muda that is added in some classifications.
Mura- the reason for muda. Unevenness and mismatch of workload, overload.
| Mura | In Industry | In IT |
| Overload | Lack of resources at peak demand, inaction in a downturn. During holiday sales, it is worth the temporary hiring additional workers. At rush hour in the subway, there are additional trains. Having won the tender, you will finish the old projects in advance so that the capacity is enough to complete the order on time. | We have no work for a month, and then we do everything within a week. This is meaningless stress topped with the discrepancy between working conditions and tasks. Placing the announcement of the event in social networks one week before the event is a failure. Marketing campaign for 3-4 months with regular posts — success. |
The seasonal, regular, controlled by advertising, consumer demand has its own rhythm, frequency (week, month, quarter). Analyze the downs and ups in demand as well as
products that are in demand or unprofitable Forecast, distribute the load and task.
Muriis inappropriate. Undue complexity in the work.
| Muri | In the industry | In IT |
| Non-core jobs | Put the sales manager to the conveyor belt shop. To appoint your third wife as director of the plant in lieu of a gift. | To Perform tasks that are not relevant to the position and developed skills. To send the layout designer to the call center. |
| Poorly staffed working place | One set of tools for 4 assemblers. | The trainee has a laptop, but there is no anti-virus program or other specialized programs necessary for the work. The designer is in possession of the obsolete pirated photoshop. |
| The Fuzzy Instructions | Abstract requirements to the order, providing measurements by eye. | «Make it that the layout has more life in it, and those buttons should be just wow!» |
| The lack of tols and equipment | One printer in the Office of the director, accounting constantly runs to print to it. | The programmer is hired with his or her own laptop and is instructed to bring it to the office as there is no option of buying a desktop computer with all the needed software. |
| The lack of proper maintenance / unreliable equipment | The obsolete conveyor belt, service guarantee that expired half a year ago. | Sysadmin does not classify and does not sign the cable in the server rack. The time on searching for a fault is multiplied several times. |
| Untrusted processes | Untested technology of processing of raw materials, the abstract proven methods of accounting and questionable ideas in production. | Monkey testing as the sole and sufficient way of testing programs for bugs (errors). |
| Poor communication | Poor audibility in the walkie talkie on the territory of the shop. The argument with the director’s secretary when it is important to urgently report on the state of emergency. The bureaucracy. | 2 mobile numbers, 8 Instant Messengers, 3 Emails and 5 social networks to get OK to do the job. |
The essence of Lean manufacturing is to eliminate all Muda, Muri, and
Mura. Understanding their causal relationship, you can focus on the origins of the
problems and avoid fixing every small detail afterward.
The advantages of the Lean methodology
A skeptic will say, why do I need Lean Manufacturing when one can simply apply a couple of standard instructions to tackle any difficulties that had already been described in state standards’ protocol or reduce wasted paper on bureaucracy in the company? The methods of lean production as a tool are strong but cannot be fully implemented without the understanding of the philosophy and structure.
It’s similar to cramming before exams just to pass it and forget all the knowledge right away. After the exam is over, you have nothing left in your brain and there is nothing to apply in practice. In the same way, when following an instruction to add a couple of algorithms that will reduce waste or deadlines to fulfill tasks, lean manufacturing cannot be created. Lean is a permanent change. Even once-a-year upgrading does not mean introducing the methodology.
The whole essence is in the experience, testing in practice. Only after personal experience, theories testing, and data collection new stages of experimentation can be analyzed and developed. Organize such cycle as a rule for corrections implementations, the fight against muda, mura, and muri.
To initially run the project on the methodology of lean, one needs:
- Gather all the information about the future task,
- Segment it to subtasks, develop and test them separately,
- To calculate time and budget on the basis of the collected experience of competitors or their own past projects (to rely only on real data instead of abstract.
The principles of lean manufacturing
On the basis of muda, mura, and muri there are exactly 10 principles of lean manufacturing:
- To eliminate waste.
- To minimize stocks.
- To maximize the flow.
- The production depends on consumer demand.
- Know the demands of the clients.
- To do it right the first time.
- To strengthen the ability of employees.
- To build a system with easy replacement of its components.
- To establish partnerships with suppliers.
- To create a culture of continuous improvement.
Also, there are three basic tasks of business. They transform the entire company:
- Purpose What customer problems are solved by the company, the ultimate value for the consumer?
- Process. What are the criteria for the assessment of each stream of values? Checking the algorithms and links of the chain, the fight against waste, inexpediency, and work overload. Each step is valuable, real, affordable, adequate, and flexible while flows and the impact are uniformly.
- People. How to allocate responsibility for each process and the flow of production? Secure the rights not after a position but after a process that is entrusted entirely to a particular person? The curator of the tasks forms the creation of value from the point of view of the business goals and actively embodies the Lean Transformation.
For individual development in the career, these same basic three objectives look the following way:
- What is the purpose of my work?
- What is the process to generate the best results in the most efficient way?
- Who are the people for whom I create value?
The notion of «Kaizen» helps finding the answers to these questions.
The principles of the Kaizen philosophy — continuous improvement
The term kaizen — consists of two Japanese characters カイゼン: Kai — change and Zen — good. Changes for the better, continuous improvement, transformation for the better... It is difficult to say whether this is the theoretical teaching of philosophers or practical management method. Kaizen symbiosis of both concepts allowing the workers to offer and then quickly test their ideas to improve the work of the enterprise. Lean transformation/ manufacturing stems from the practical part of and is based on its philosophy.
Kaizen is based on five pillars:
- Equal interaction at all levels (leadership, managers, and workers) and direct communication among them.
- The individual discipline
- A healthy moral state of the team and each individual.
- Quality circles
- Suggestions for the workplace and conveyor from the workplace and conveyor belt to the method of company’s work evaluation.
Read more about Kaizen in the next article.
The algorithm of lean production implementation
According to James Womack, Founder of the Lean Enterprise Institute and author of several books on transformation:
- Select a leader — responsible conductor of change.
- Obtain knowledge about lean and kaizen from a reliable source.
- Find or create a crisis — a problem that requires an immediate action.
- Experiment, practice, analyze the results immediately. Do not get too deep into developing a strategy (it has been confirmed by the Wright Brothers).
- To build real and desired maps of value creation flow. They should differ.
- To ensure the transparency of the results for all staff.
- To reduce the production cycle (the acceleration of the flow).
- Implement Kaizen and continuously develop the company (the creation of value in the shops goes to the administrative change).
Here is what to begin with when it comes to the introduction of lean production. The possible tools:
- Value Stream Mapping
- Pull production
- Kaizen
- The 5C
- SMED
- Poka Yoke
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- Just-In-Time (JIT)
- Visualization
- The U-shaped cells
Implementation examples of lean manufacturing
Competitiveness of the company often depends on certain criteria. Fast delivery of tasty pizzas will win over the most delicious pizza. Customization of the vehicle at auto dealership is more appealing than a standard model. Detailed results of the private clinic’s medical analyzes is always better than the minimum of information provided by the clinics on the go.
To provide an advantage over competitors (speed, customization, the quality of the research) can be done by continuous improvement of the project management system as done many companies in the world.
Lean have been successfully implemented:
- In the United States: Toyota, Alcoa, Boeing, Pella, Emerson Electric, Jacobs Equipment Company (Danaher).
- In Europe: Motoman Robotec, Unior, Iskra Asing, Volvo, Metso, Nuon.
- In China: Lenovo, Suntory.
- State and municipal agencies of many countries.
Applications and tools of Lean
Implement the transformation into a modern company is easier than 30 years ago.There are many similar applications for Android and iOS that help lead economical and quality-oriented business.
The tools of lean manufacturing are used to motivate staff, build relationships and network between the shop and the leadership, analyze the results of the introduction of new ideas and the discovery of wastes in the work of the enterprise. Testing and experiments, developing a system of conveyors or bugtrackers for programmers — all of this is soft for Lean methodology
Worksection
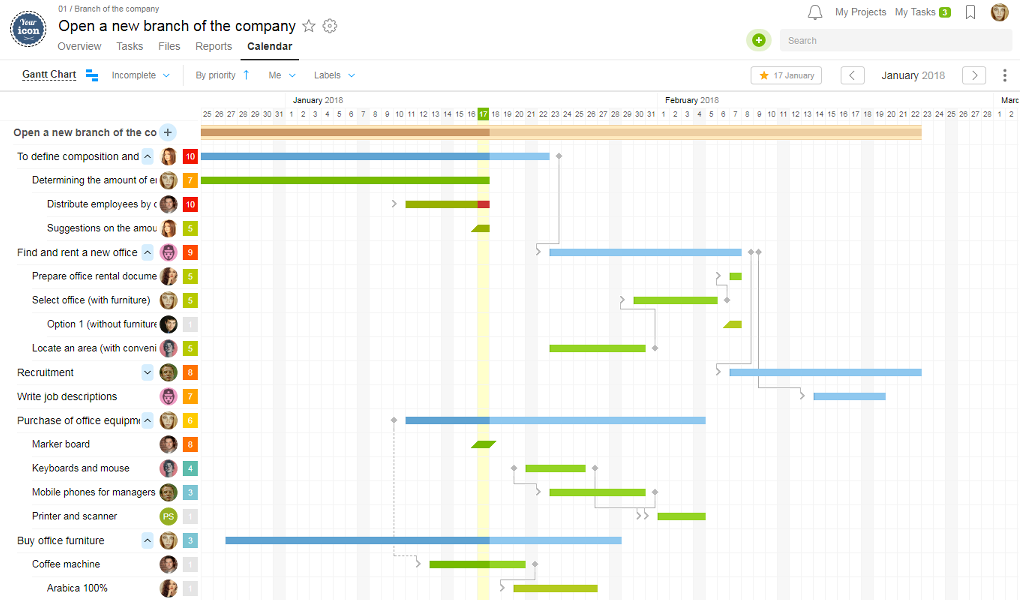
Worksection — Saas service has fully functional management, Gantt and several types of reports.
The Gantt chart allows you to track the relationship, the chronology of tasks, and people who were assigned as responsible for them. Records have overdue tasks and exceeded budgets marked.
In the task section «by people», executives can see the scope of work for each person as well as if there are people who have been idle. It is so easy to identify improper distribution of human resources. This way the fight against muda, mura, and muri becomes clear and simple.
You can create a separate «proposals from the command» project where tasks can be created for all the ideas to be implemented.
You can also set the deadline for two weeks or a month, test the idea, discuss it in the comments of the process, and then analyze the results.If the idea is good — implement it fully.
Oracle

Most business owners apply programs like Oracle or virtual services for project management.
LeanApp
The most famous application is LeanApp for iOS that allows you to organize and control
all processes in the company.
The verdict
Companies implement Lean Manufacturing throughout the world, but not all of them are flourishing thanks to it. Many people do not know how, or do not understand the philosophy, or incorrectly apply provided instructions.
The essence of the methodology:
- Eliminating waste,
- The empowerment of workers,
- Reducing stocks,
- Increasing productivity.
The way is always individual, and it depends on many factors, such as the industry and market segment, target audience, product or service itself, priority, and competitive difference of the company.
Beginning the fight with waste in most «narrow» places of work flow where the error is critical.
Finding the crisis and solving it is much more efficient than mindlessly implementing the Lean algorithm.