Planning is the foundation on which any project is built. The stronger it is, the greater
the likelihood that the project will be successful. This is the reason for the project
management plan that consists of three blocks: activities (objectives, concepts of the
project, resource uses and etc.), tasks and resources (people, equipment, money, etc.).
What is the project management plan?

Project management plan is a document that specifies all elements of the project: from the activities and resources to the evaluation criteria of success and risks. When developing the plan, project manager tries to cover the entire project, from initiation to closing.
Project management plan is the most important document when creating a project (at the level of stakeholder involvement). Similar to how a project cannot be implemented without the participation of the stakeholder, a project will fail without a sound management plan. Such documents as the management plan for the cost, time, quality, risk, resources, etc. are all parts of an extensive management plan.
In traditional project management, a plan provides for restrictions on all five stages: The start, planning, execution, monitoring and completion. Projects on the concept of Agile cannot be planned until the very end due to the nature of the work by a flexible model.
Therefore, the plans are developed and approved in the course of the life cycle of the project.
Usually the project has two management plans:
- Basic — approved by the leadership (customer). It is determined by the success of the completion of the tasks that are controlled by timing and quality.
- Working — unlike the previous one, the project manager makes changes according to the new information or tasks.
What is it for?
A good project management plan should answer the basic questions:
- Why? — What problem the project solves and what’s its value? Why the project is sponsored?
- What? — What are the main products (delivery) of the project? What needs to be done for the successful completion?
- Who? — Whom to bring to work on the project and for what each of the participants will be responsible? In what format will they be organized?
- When? — What are the time frame of the project? When will the key moments/milestones be fulfilled?
Milestone — reference point during the project (for example, the transition to a new iteration).
Objectives of the Project Management Plan are:
- The coordination of participants’ actions — these include not only the project team directly but also stakeholders. The larger the project, the more difficult it is to establish a workflow process.
- Tracking the status of the project implementation — if the traditional management has a rigid sequence of steps, the project management increasingly uses varieties of Agile-model where the project is divided into small working pieces.
- A clear understanding of one’s role in the project — this, by the way, what programmer Rick fromthe viral article"We fired our top talent. Best decision we ever made" was lacking.
- Searching problematic areas of the project before the phase of the active development — long-term projects suffer the most from such «sores». In the Agileconcept, the problem is partially solved by constant testing and searching for vulnerable places for further corrections.
The key components of the project management plan

Compiling management plans for projects based on one template will not work; however, there is a set of basic elements and knowing them, it is easy to build a skeleton of the future project:
- a brief description of the plan — a couple of paragraphs about the key elements of the project that are revealed in the plan.
- the strategic and organizational alignment — this includes the results of theanalysis of the stakeholders and organizational objectives that be supported in carrying out the project.
- defining the scope of the project — this part includes the following elements:goal and objectives, expected results, and PBS and WBS tools. In this section, it is also important to write out the quality specifications — the criteria for theeffectiveness of the product or services from the customer’s point of view.
PBS (product breakdown structure) is a tool for analysis, documentation, and transfer of project results. PBS is a part of the planning method based on the product (one of the main methods in the model of PRINCE2 project management).
WBS (work breakdown structure) is a hierarchical breakdown of project work into smaller tasks (operation) up to the point where ways of work execution are clear, there is a possibility for assessment and planning.
- assessment of the feasibility and contingency plans — provides an assessment of the economic, technical, and organizational feasibility of the project execution along with identification and analysis of risks; offers plans of action in critical situations to eliminate risk factors.
- restrictions — a list of known limitations imposed by the environment or leadership (fixed budget, lack of resources, etc.).
- requirements for the project team — the project team rganization: the roles and responsibility of the participants. Training requirements are also written out here.
- material requirements — includes elements of space, hardware, software, and other resources for the completion of the project.
- schedule and milestones — this section defines the milestones and schedule for the activities of the project including three key elements: Delivery (work results), the date or duration, and critical dependencies.
- budget (cost estimates) — the expected costs are normally divided into three types: capital (buy stock for storage of products), expenses (weekly purchases of materials for the workpiece) and labor (salary of team members).
- risk management — a detailed description of the process for risk management: from the identification (through brainstorming, interviewing, SWOT analysis) to selecting the monitoring system (pro-or reactive).
- change management — similar to the previous item but is only related to changes (and there will be a lot). It is worth to write out the algorithm changes execution, management methodology (ADKAR, AIM and others), the formula of calculation of success changes probability, etc.
- communication management — this item applies to the team and stakeholders. Project manager in this section should describe the communications system that will be used and the channels of documentation transfer on project performance of the parties of the project.
- attachments — this can be any documents: from the individual notes to presentations and certificates.
The list of sections of the plan is supplemented depending on the characteristics of the
project.
The basic and working project plans
During the work on the draft project manager, the team members and stakeholders
work with two types of plans:
- basic — primary, stable, approved by the customer or other pre-specified people, agreed with all stakeholders.
- working — version of the basic plan, which displays the changes in timing, cost, other parameters of the project.
In the course of development of the project, you can compare the basic and working
plans, understand where the «slack» work is and where, on the contrary, the
implementation of the project goes faster (more economical) than originally thought. In
rare cases, the changes in the course of the project shall be entered in the basic
management plan.
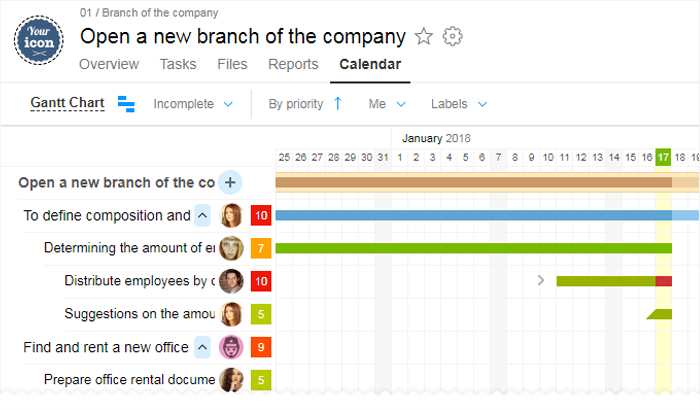
In the Worksection, Gantt chart allows to see the difference between the basic and the working plan (blue — the total time, red — overdue tasks, green — tasks completed on time)
Developing a project management plan
As is the case with the key elements of the project management plan, there is no one correct algorithm of its development.
We have designed a simple step-by-step procedure for writing the plan, consisting of 16 items:
- Determine the starting conditions to develop a plan- it is important to understand, with whom you will develop it (by yourself, with the participation of the leadership, stakeholders), where and when, and so on. It is essential to prescribe methods (for example, brainstorming) and software (such as Microsoft Visual Studio), which will be used in the creation of the plan — this significantly saves time and simplify the task.
- Determine the initial conditions of the project — the part that describes the content of the draft, the list of requirements to the results and its management. For example, the project was conceived for the sale of high-quality neon fidget spinners with he images of superheroes. As a result of the successful implementation of the annual project, there should be 100,000 units of goods sold within 12 months from the start of the project, then the business will be sold. The structure of the project management will consist of the project manager in the central office and the relevant departments in the regional offices of the project.
- Divide actions performed into such that will be performed by the project team and outsourcing.
- Create a project WBS, breaking it down into smaller manageablepieces. This is similar to the agile approach, when the full code is divided intomany small pieces of work.
- Set a series of tasks for each part of the WBS and build the relationshipbetween them. This way the task of purchase and construction of a regionalwarehouse for the storage of fidget spinners can only be performed after the analysis of the market and the sale of a certain quantity in a particular area.
- Identify the necessary competences to perform each task. Here it is important not to fit the required knowledge and skills to potential participants of the project but focus on the «ideal» requirements.
- Estimate the time and money to perform tasks.
- Develop the critical pathproject. Technique is good just for the grocerybusiness, and it is easy to display through the scheme (for example, the Ganttchart).
- Create a calendar plan for the project — primary, intermediate, final dates. For example, a simplified diagram: November 1, start the project, December 1 — startthe sales for the New Year, December 31 — summing up the Christmas sales,January 15 — special product launch for the St. Valentine’s Day, February 20 — summing up and so on.
- Calculate the cost of the project (in our case, how much will it cost to successfully sell 100,000 fidget spinners and then sell the business).
- Specify quality requirements (for example, the prescribed standards of quality workmanship for fidget spinners).
- Assign responsibility to specific people on the task. This is where item 6 comes in handy, whose list will serve to bind the competence of team members.
- Plan the format of work with stakeholders — find the channels of communication, determine the degree of their involvement in the project, and soon.
- Calculate the risks (for example, the formula of the cumulative method). In our example with fidget spinners, this can be a simple market glut, a violation of the terms and conditions of freight forwarders, etc. In the analysis of the risks, use data from the preceding items.
- Note the limitations of a project to make corrections to the projec management plan. In our case, the parts of the fidget spinners are delivered from China, assembly occurs in Ukraine, and it already limits the ability to control the quality of the materials and quick conversion.
- Go through all the items of the plan again in order to achieve Zen. What’s left is to finalize is the procurement list and its requirements, run by stakeholders — and you have a ready-to-go project management plan.
The cumulative method of calculating risks — method of risk factors evaluation that may hinder getting the planned income. In constructing the discounting rate by this method, the risk-free rate of return is taken as a basis with the added rate of return for the investment risk into the project or company.
The approval of a project management plan
In the «Stop paying for everything» book, Vladislav Gagarsky sets the following approval scheme as an example:
- The team leaders send a jointly developed plan to the project manager.
- The leader approves the project management plan or, in case of errors,
- The project leader sends the approved plan to the leaders of the project teams for further implementation.
But the scheme is more suited for well-established staff that performs several projects one after the other or has changed their usual activity. For those who decide to write and approve the project management plan from scratch, the method will not work. In such cases, the basic project is approved by the company director or the project owner (customer) with the advice of the project manager.

Tips on how to create a project management plan:
- write out the plan in the material form — it doesn’t matter whether it will be doneon paper or using a special software. Even the smallest nuance should be spelledout, otherwise, wait for problems with communication between the participantsand stakeholders.
- attract stakeholders to the plan creation — establishing communication with them, you will avoid problems with the formulation of a shared vision of the project and the expected results.
- organize your document management system — projects generate a huge number of documents: the primary concepts, ideas, designs, presentations, risk management plans, the diagram of the critical path, and so on. They fall into the basic and working plans for the management of the project. For easy access and fast implementation, there should be a clear system of the documents.
- explore the details before developing a plan — to paraphrase Ostap Bender’s from the famous «The Twelve Chairs»: «In the morning — research, in the evening — plan. Or plan in the evening, research in the morning». Learn expectations of customers, participants of the project, expected project objectives, techniques that are worth to apply when developing a project management plan. This preliminary work will reduce time costs and, most importantly, will minimize the number of errors in the project management plan.
- talk with the team before the start — this way you will have updated knowledge about the competencies of employees and see if there is interest in the future project. No wonder the following is of the principles of Agile-Manifesto: "Project work should be done by motivated professionals. In order for work to be completed... trust them".
The verdict
Project management plan is not your magic wand.
Initially, it will be the declaration without tools to implement it. And the tool that can be used for it is Worksection with its projects/tasks/subtasks and money, time, and executives accountability right there in the tasks. This is the best way to organize visible work of the company where the link between basic and working plans is obvious to all.