Today we will discuss the difference between goals and objectives, which is important to understand. Knowing this will make it easier to plan your business and achieve results.
- Goals give us a final image of what we want to achieve. They guide and motivate us.
- Objectives are measurable and time-bound. They serve as milestones on the way to the larger ambitions.

We’re gonna discuss in detail roles in both personal and professional contexts. And also provide you with the clear difference between goals and objectives. Because we are sure that deep understanding of goals and objectives leads to more effective strategy development, business planning and project navigation.
Types of goals
Goals have different types and can be divided into multiple categories. Each kind has its own set up for achieving and kind of approach. Among these types we can highlight time-oriented, outcome-oriented and process-oriented goals.
Deep understanding of their difference could level up strategy development. This can lead to building a more effective working process to achieving success.
Time-based goals
Time-based goals are those that are tied to specific deadlines. For example, to complete a project in six months or to hire 3 more employees in less than a year. They create urgency and help keep focused on getting things done.

The deadlines serve multiple purposes:
- Task prioritization. Deadlines assist in arranging tasks based on their importance, ensuring critical projects are addressed first.
- Enhancing efficiency. The sense of urgency from a deadline can lead to increased efficiency, driving teams to meet specific targets within set timeframes.
- Optimized resource management. Deadlines require strategic planning and wise use of resources.
- Monitoring project progress. They allow for consistent tracking of a project’s advancement, ensuring it stays on schedule.
- Aligning team efforts. Deadlines are vital for aligning the efforts of team members, particularly in complex projects with interlinked tasks.
Outcome-oriented goals
What type of goal is focused on the end result? It is outcome-oriented goals. This type of goal is focused on achieving a specific result or end state. Most of the cases the result is supposed to be quantifiable.

For instance, a company sets an objective to increase its revenue by 20% in the upcoming year. Or a product team aims to improve customer satisfaction ratings by 20% over the next six months.
These goals are strong motivators. They set a clear target, defining what needs to be achieved. This clarity gives direction and purpose, crucial for business strategies. It helps in focusing resources and efforts effectively towards achieving specific outcomes.
Process-oriented goals
Process-oriented goals underscore the significance of the steps taken to reach a final result. They focus on establishing productive workflows. Additionally, they involve upholding key procedures vital for reaching project targets.

For instance, a company team aims to cut project completion time by 30% in a year. Another variant where a business plans to adopt agile methods like scrum or Kanban within six months to boost flexibility.
These goals are vital to long-lasting business success. They highlight the importance of building and reinforcing practices. These practices and actions are crucial for achieving overall project or business purposes.
How to measure goals
Goal measuring helps in tracking progress. You can use various methods for it. These include closed-ended questions, scoring systems, and rubrics.
Ask a closed-ended question
Closed-ended questions are a direct and easy way for measuring. They require straightforward answers such as «yes» or «no».
This method is especially effective for simple work tasks where progress can be clearly defined. Because you can quickly assess whether you are meeting the purposes.
Use a points system
A point system measures progress in numbers. It involves giving numerical values to various parts or steps of a goal, making it easier to measure progress.This method is useful for complex tasks that have multiple components. As it allows a more differentiated evaluation of the completion of each part of the process.
Follow a rubric
Rubrics provide a detailed and systematic way to measure goals. They provide a set of criteria and standards for different levels of performance.Rubrics are widely used in education and are adaptable to a variety of contexts, including business and project coordination.
Types of objectives
Objectives are key to the achievement of any goal.
They can also be categorized into different types. For example, strategic, tactical, and operational objectives. Each type has a different role in the working process.
They can also be categorized into different types. For example, strategic, tactical, and operational objectives. Each type has a different role in the working process.
Strategic objectives
Strategic objectives are like the big-picture goals that match up with the long-term vision and main plan of a company. They guide the company’s overall direction. Also, this type is usually broad in scope and has a long-range focus.

Strategic objectives might include a business plan to break into two new international markets in the next two years. Or a company wants to launch three innovative products in the next three years.
Tactical objectives
Tactical objectives are more specific and action-oriented. They turn big goals into practical plans, acting as a link between long-term objectives and everyday tasks. These are typically mid-term and more specific.
Such as boost sales performance in the next quarter or an increase in market share in a particular region.
Operational objectives
Operational objectives are focused on the day-to-day activities and processes that help achieve tactical and strategic aims. They are short-term, highly specific and often involve routine tasks.

For instance, aiming to make more products each day by a set percentage, or cutting down on costs by finding ways to work more efficiently.
How to measure objectives
It’s important to make sure that objectives are being met and helping to achieve the main target. Measuring objectives can be done by assessing results achieved, using qualitative survey data, and comparing past and current performance.
Measure attainment
This means checking how much of the objectives have been met. It’s a simple way of comparing the results with the set purposes to see how efficient a team is.
Measure qualitative data with surveys
Surveys are a great tool for gathering qualitative data related to objectives. They can provide insight into subjective aspects such as customer satisfaction, employee morale, or market perception.
Measure past performance vs. Current performance
Comparing performance is an effective way to measure progress. This method helps identify trends, improvements, or areas that need more focus.
Errors in formulating goals and objectives
Formulating goals and objectives is a critical process, and errors can lead to ineffective plans and strategies. Common mistakes include:
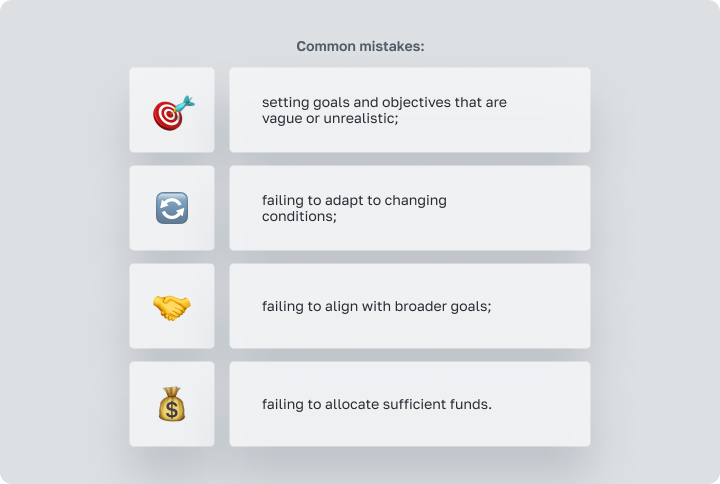
Avoiding these mistakes requires setting clear goals and objectives. Check and change your workflow, based on what you have now and what you want to achieve in future.
Goals vs Objectives examples
Practical examples help you better understand the concepts of goals and objectives.
Example 1: for Software development
Goal: Successfully launch a new software product within 18 months.
Objectives:
- Complete the market analysis and define software requirements within the first 3 months.
- Develop a prototype of the software in 6 months.
- Conduct beta testing with select customers by the 12th month.
- Finalize and launch the software by the end of the 18th month.
Example 2: Management for office relocation
Goal: Relocate the company office to a new location within 6 months without disrupting ongoing operations.
Objectives:
- Identify and finalize the lease for a new office space within the first month.
- Plan and execute the interior setup and infrastructure development in 3 months.
- Transition all departments to the new location seamlessly over a period of 2 weeks, ensuring minimal disruption to work.
- Complete the entire move and resume full operational capacity in the new office within 6 months.
This example focuses on the complex goal of relocating an office. The objectives break the destinations down into specific tasks, such as securing a new space, setting it up, and moving departments. All of this is done within a strict timeline to minimize disruption.
Example 3: Management for marketing campaign
Goal: Increase product sales by 30% over the next quarter using a targeted marketing campaign.
Objectives:
- Research and identify the target market and customer preferences within the first two weeks.
- Develop and launch a marketing campaign within the first month.
- Monitor and analyze campaign performance weekly and adjust strategies as needed.
- Achieve a 30% increase in sales by the end of the quarter.
These real-life examples show how important it is to set and reach goals and objectives effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, the difference between goals and objectives is critical to successful planning and execution in any field. Goals and Objectives not only frame where we want to go, but also map out how to get there. While goals set the direction and end destinations, objectives describe the specific, actionable steps needed to achieve those destinations. This dynamic of goals and objectives is essential to maintaining focus and driving progress.
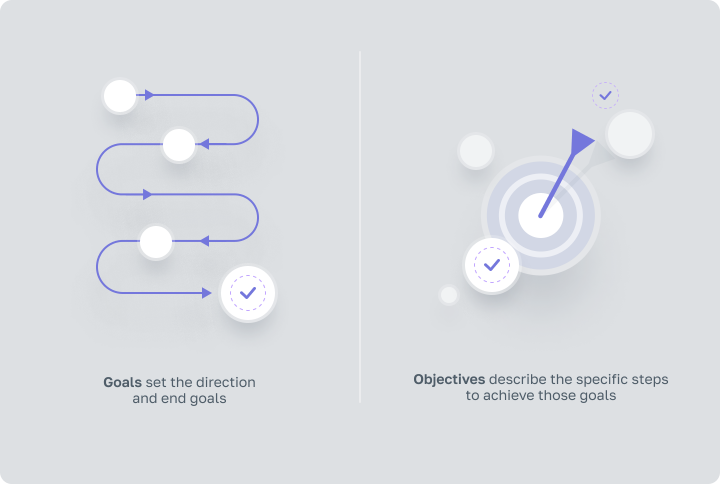
Moreover, the manner in which we measure the progress of our goals and objectives can significantly impact their successful attainment. Goals and objectives are not mere checkpoints; they require adaptability and a willingness to evolve as situations change. By embracing this fluid relationship between goals and objectives, individuals and organizations can ensure they remain on the path to success, constantly aligning their actions with their overarching ambitions.