In today’s business landscape, understanding what OKRs and KPIs are is crucial for molding strategic management processes and enhancing organizational effectiveness.
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) focuses on setting clear, measurable goals that drive teams towards specific outcomes. OKRs consist of an Objective, which defines a clear direction or overarching goal, and Key Results, which are measurable milestones under each objective that track the progress towards these goals.
For example, an objective might be to grow the business, while the key results could include increasing customer retention rates by 10%, achieving a revenue growth of 20%, and expanding into two new markets within the fiscal year.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are metrics used to evaluate the success of an organization or a particular activity in which it engages. Unlike OKRs, which are often set and reviewed quarterly or annually, KPIs tend to be more static, providing ongoing monitoring of performance against critical benchmarks.
For example, common KPIs include net profit margin, return on investment, and customer satisfaction rates.
Understanding the difference between KPI and OKR is crucial:
- OKRs focus on setting and achieving specific objectives to drive progress and foster innovation;
- KPIs are metrics used to assess the effectiveness of current operations in achieving key business outcomes.
Understanding the Basics
What Are OKRs?
OKRs are a common goal protocol that teams and individuals use to establish demanding, ambitious goals with measurable outcomes. Typically set on a quarterly basis, OKRs are designed to motivate employees to be top performers in their roles and to align their performance directly with the company’s strategy. The methodology streamlines processes and ensures that all team members understand the strategic plan and their role in it by linking company, team, and personal goals to measurable results.
Core principles of OKRs include:
- Aspirational Goals: OKRs are unique in their emphasis on setting stretch goals. These goals challenge teams to go beyond standard expectations. These goals are aspirational and designed to push individuals and teams out of their comfort zones in order to foster innovation and significant growth within the organization.
- Measurable results: Each of the objectives in the OKR must be paired with clear, measurable key results. These are quantifiable outcomes that measure the success of the goal, not just activities. Being measurable ensures that each team member can objectively assess whether they are on track to meet the goals or need to adjust.
- Alignment and transparency: OKRs foster an open environment. Goals and progress are visible to everyone in the organization. This transparency ensures that everyone is moving in the same direction and helps align efforts across teams and departments. It encourages collaboration. Employees can see how their efforts contribute to the broader goals of the organization.
- Frequent monitoring and updates: In contrast to traditional annual or semi-annual reviews, OKRs require regular check-ins to assess progress. These frequent assessments allow teams to stay agile. They can adjust their strategies as needed to stay in line with overarching business goals. It also ensures that the organization is able to respond effectively to changes in the competitive landscape or shifts in internal priorities.
What Are KPIs?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial tools in assessing an organization’s effectiveness in reaching its strategic targets. These quantifiable metrics are utilized not just to reflect on past performances, but to gauge ongoing operational achievements against set business objectives. With their comprehensive application, KPIs play a pivotal role in strategic, financial, and operational enhancements, guiding companies toward optimal performance levels.
Core Aspects of KPIs:
- Quantifiable Metrics: KPIs transform abstract performance levels into concrete, measurable data. This attribute is fundamental, as it quantifies successes and challenges in a format that is straightforward and universally understandable within the business.
- Standardized Measurements: KPIs allow for consistent measurement across timeframes and against peers and industry standards. This standardization supports objective assessment and benchmarking, providing a clear frame of reference for evaluating company performance both internally and in comparison to others within the industry.
- Actionable Insights: The power of KPIs lies in their ability to furnish actionable insights. These insights guide strategic decision-making, illuminating areas that require improvement or adjustment. Effective KPIs act as navigational beacons, showing where a company is on its path to achieving its long-term goals.
- Operational Improvement: Beyond strategic implications, KPIs are instrumental in refining day-to-day operations. Regular tracking of these indicators helps identify operational bottlenecks and highlights efficiency gains, driving continuous improvement across all levels of the organization.
- Focus on Critical Success Factors: KPIs direct attention to areas that are critical for the organizational success, ensuring that resources are allocated and efforts are directed towards those activities that are most likely to achieve significant, positive impacts on the company’s performance.
Comparative Analysis
Differences Between OKRs and KPIs
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are both central to an organization’s strategy and performance measurement, but they serve different purposes and are implemented in very different ways. An understanding of these differences is critical for any organization whose goal is the implementation of a robust performance management system.
 Purpose and Focus
Purpose and Focus
- OKRs aim to drive change and foster innovation by encouraging teams to aspire beyond their current capabilities. OKRs are typically qualitative and often focus on project completion or launching new initiatives.
- KPIs are quantifiable metrics that often emphasize consistency and maintenance of performance standards.
 Time Frame
Time Frame
- OKRs are often set on a quarterly basis, allowing organizations to adapt and change quickly to meet evolving strategic goals. This shorter cycle helps organizations stay agile by continually reassessing and adjusting their objectives.
- KPIs tend to be tracked over longer periods to evaluate performance trends and organizational health, providing insight into whether a company achieves its long-term operational targets.
 Scope of Measurement
Scope of Measurement
- OKRs encourage employees and teams to push the boundaries of what is possible, fostering innovation and significant advancements. They are about setting and achieving specific objectives that contribute directly to the company’s strategic plan.
- KPIs measure ongoing operations and are used to gauge the standard operations of an organization. They help ensure that the day-to-day activities align with and support the company’s broader strategic goals.
 Alignment and Transparency
Alignment and Transparency
- OKRs are designed to be transparent and align disparate teams towards unified organizational goals. Everyone in the organization should understand the OKRs and see how their contributions move the needle.
- KPIs may not require as much transparency across all levels, but need clear communication within specific teams or departments concerned with the particular processes these KPIs measure.
 Flexibility and Adaptation
Flexibility and Adaptation
- OKRs can be adjusted more frequently due to their short-term nature, which allows companies to pivot or change strategic directions with more agility.
- KPIs are usually more stable metrics that change less frequently, providing a consistent benchmark for performance over time.
Examples of OKRs and KPIs in Practice
We’ve prepared some examples based on well-known companies. They illustrate how companies can use OKRs and KPIs.
 OKRs in Practice
OKRs in Practice
Google: Perhaps the most famous adopter of OKRs, Google has used this framework to fuel its explosive growth. An example of an OKR at Google might be:
Objective: Improve the speed of the search engine results page (SERP).
Key Results
- Reduce the average load time of the SERP by 0.2 seconds.
- Increase user satisfaction with SERP loading times by 10% as measured by surveys.
Objective: Increase global market presence.
Key Results
- Expand operations into three new countries.
- Achieve a 25% increase in international revenue.
 KPIs in Practice
KPIs in Practice
Amazon Known for its customer-centric approach, Amazon closely monitors several KPIs to ensure efficiency and customer satisfaction. - An example of a KPI at Amazon would be the “Order Defect Rate” (ODR), which measures the percentage of orders that result in negative feedback, an A‑to‑Z guarantee claim, or a service credit card chargeback. Keeping this rate low is crucial for maintaining customer trust and satisfaction.
Salesforce This company relies heavily on customer success KPIs, such as “Customer Lifetime Value” (CLV) and “Customer Churn Rate.”
- By monitoring these KPIs, Salesforce ensures that they are not only acquiring customers but also retaining them, which is vital for long-term growth.
 Integrating OKRs and KPIs
Integrating OKRs and KPIs
- Adobe After abolishing annual performance reviews, Adobe introduced OKRs to drive performance and clarify expectations. They use KPIs like “Customer Retention Rates” and “Product Development Cycles” alongside OKRs to ensure that while they strive for ambitious quarterly goals, they also maintain high standards in customer satisfaction and innovation cycles.
- Zalando Europe’s leading online fashion platform uses a blend of KPIs and OKRs to streamline operations and boost growth. For example, an OKR to “Expand market reach in European countries” is supported by KPIs measuring website traffic, conversion rates, and customer acquisition costs in new markets.
This dual approach not only aligns with overarching business goals but also ensures that day-to-day operations propel the organization towards these goals effectively.
Strategic Implementation
Integrating OKRs and KPIs in Business Strategy
Integrating Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) into a business strategy involves a sophisticated approach. Here is an expanded strategy for effectively using both OKRs and KPIs:
- Strategic Alignment: Begin by ensuring that both OKRs and KPIs are intrinsically aligned with the organization’s long-term strategic goals. This involves setting OKRs that push the organization towards ambitious achievements and using KPIs to monitor ongoing performance, providing real-time feedback on progress towards these goals.
- Driving Change with OKRs: OKRs are designed to foster significant change and progress within the organization by setting highly ambitious and seemingly unreachable goals. This approach is particularly beneficial for projects requiring innovation and substantial transformation, as it encourages teams to exceed conventional expectations and think outside the box.
- Maintaining Stability with KPIs: Unlike OKRs, which are generally aspirational, KPIs should be used to ensure consistent and steady operational performance. KPIs are typically more static and focus on maintaining and slightly improving key business processes to ensure the organization’s backbone remains robust and reliable.
- Enhanced Transparency and Communication: It is crucial for the success of OKRs and KPIs that they are clearly communicated across all levels of the organization. Transparent communication ensures that every team member understands their role in the broader context of the company’s goals and how their individual efforts contribute to these objectives.
- Dynamic Reviews and Adaptation: Incorporate regular and systematic reviews of both OKRs and KPIs to ensure that the organization remains on track to achieve its goals. These reviews provide an opportunity for mid-course corrections and allow for the adjustment of strategies in response to evolving business dynamics or unexpected challenges.
- Iterative Improvement and Feedback: Encourage a culture of feedback, where insights and observations about the OKR and KPI processes are regularly solicited and valued. This feedback loop can lead to improvements in how goals and performance metrics are set and evaluated, fostering a proactive environment of continuous improvement.
- Integration of Advanced Analytics: Utilize advanced data analytics to deepen the understanding of OKRs and KPIs performance. Analytics can provide predictive insights and nuanced analysis of trends, helping to refine goal-setting and performance evaluation processes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Implementing Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) within an organization comes with significant potential to drive performance and align with strategic goals. However, certain pitfalls can hinder their effectiveness. Here’s a more detailed look at common mistakes organizations make and how to avoid them:
- Misalignment with Strategic Goals: One of the most prevalent issues in implementing OKRs and KPIs is the lack of alignment with the broader organizational objectives. Strategic misalignment can lead to efforts that are counterproductive and do not contribute to overall business success.
- Overcomplication: Simplicity is key in setting OKRs and KPIs. When these metrics are too complex, they become difficult to understand and follow.
- Cultural Misalignment: The organizational culture must support the methodologies behind OKRs and KPIs. This includes fostering an environment that emphasizes transparency, embraces continuous feedback, and promotes accountability.
- Inadequate Communication: Communication plays a pivotal role in the successful implementation of OKRs and KPIs. Without clear communication about the purpose, process, and progress of these goals and indicators, there can be a lack of buy-in or engagement from the team. Ensuring that all members understand the metrics, how they contribute to them, and the overall benefit to the organization is critical.
- Static Measures: The business environment is dynamic, and so should be the approach to OKRs and KPIs. Treating these metrics as static often leads to outdated goals that no longer align with the business’s current needs or market conditions. It’s essential to regularly review and update OKRs and KPIs to reflect new challenges, opportunities, and strategic shifts.
- Lack of Review and Adaptation Processes: Successful implementation requires continuous monitoring, review, and adaptation. Organizations should establish regular check-ins to evaluate the relevance and effectiveness of OKRs and KPIs. These reviews can help identify areas for adjustment, ensuring that the metrics remain relevant and drive the desired outcomes.
- Ignoring Employee Input and Feedback: Failing to involve employees in the setting and evolution of OKRs and KPIs can lead to decreased motivation and engagement. Employees often have insights into potential improvements and obstacles on the ground. Incorporating their feedback can enhance the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and increase overall buy-in.
Maximizing Business Performance
Using OKRs and KPIs for Growth and Improvement
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are central to strategic business operations that enhance productivity and streamline processes across various business levels. By effectively deploying OKRs and KPIs, organizations can significantly boost their growth trajectories and operational efficiencies. Strategic Alignment and Focus
Strategic Alignment and Focus
OKRs drive strategic alignment by connecting team efforts to overarching business goals. They challenge organizations to set and pursue bold goals that go beyond what is normally expected, and in doing so foster innovation. This helps organizations navigate complex environments and remain competitive by ensuring that every team effort is focused on tangible business impact.
 Enhanced Performance Measurement
Enhanced Performance Measurement
KPIs are vital for ongoing performance assessment. They provide critical data points that organizations use to gauge their effectiveness across various functions, from sales and marketing to production and service delivery. By setting specific and measurable indicators, businesses can track their progress against industry benchmarks and internal targets, making necessary adjustments to strategies and operations. This continual measurement feeds into a refined decision-making process, enhancing overall business agility.
 Encouraging Agility and Responsiveness
Encouraging Agility and Responsiveness
The dynamic nature of OKRs encourages businesses to remain agile, adapting swiftly to changes in the external market or internal operations. Regular OKR cycles prompt reviews of strategies and goals, allowing companies to pivot or redirect resources as needed. This agility is particularly crucial in today’s fast-paced market conditions.
 Driving Employee Engagement and Motivation
Driving Employee Engagement and Motivation
OKRs and KPIs significantly impact employee motivation and engagement. By clarifying goals and the means of achieving them, these frameworks help employees see the value of their contributions, enhancing their commitment to organizational objectives. The transparency and clarity provided by OKRs and KPIs ensure that employees at all levels are aligned with the company’s vision and understand their roles in achieving it.
 Continuous Improvement
Continuous Improvement
Institutionalizing OKRs and KPIs cultivates a culture of continuous improvement. Organizations become adept at identifying performance gaps and areas for enhancement. By leveraging regular feedback and iterative goal-setting, they can foster a proactive environment. This not only improves current processes but also drives innovation, as employees are encouraged to think critically and suggest improvements.
 Balancing Long-Term Vision with Immediate Results
Balancing Long-Term Vision with Immediate Results
OKRs help balance the focus on long-term strategic goals with the urgency of achieving immediate results. This balance is critical for maintaining a steady pace towards achieving big-picture outcomes while ensuring that day-to-day operations are optimized for efficiency and effectiveness.
Organizations can improve their strategic execution and become more adaptable, focused, and competitive in their respective industries by fully understanding and leveraging the strengths of both OKRs and KPIs.
Case Studies: Success Stories of OKRs and KPIs
The strategic implementation of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) has driven substantial benefits in diverse sectors, including technology, retail, and financial services. Here’s a deeper look into each case:
- Tech Industry Innovator: A prominent technology company leveraged OKRs to expedite its product development processes and expand its market presence. The organization established clear objectives aimed at increasing feature rollouts and boosting user engagement metrics. These objectives were directly linked to measurable key results, enabling the company to systematically enhance its product offerings. As a result, it observed a substantial increase in customer satisfaction and retention rates. The strategic use of OKRs helped in aligning product development efforts with user demands and market trends, facilitating rapid adaptation and innovation.
- Global Retail Chain: A globally recognized retail chain utilized KPIs to refine its supply chain management and cut overhead costs. Key performance indicators focusing on inventory turnover rates and logistics efficiency enabled the company to identify inefficiencies and optimize processes. This strategic monitoring and adjustment led to more streamlined operations and significantly improved profitability, particularly vital during a challenging period for the retail industry. The application of KPIs provided a data-driven approach to operational management, ensuring resources were used efficiently and effectively.
- Financial Services Firm: A financial services firm adopted an integrated approach using both OKRs and KPIs to elevate its customer service standards. The firm set OKRs with the aim of enhancing customer satisfaction levels, while KPIs were used to track daily service interactions and resolution times. This dual approach fostered an environment focused on continuous improvement, leading to higher client retention and an increase in new client acquisitions through referrals. The alignment of customer service objectives with measurable performance indicators ensured that the company’s client-handling capabilities were consistently optimized for excellence.
- Healthcare Provider: A healthcare organization implemented KPIs to track patient outcomes and treatment efficiency. They focused on reducing wait times and improving patient follow-up rates. By analyzing these indicators, they were able to streamline appointment scheduling and enhance patient care protocols, significantly improving patient outcomes and satisfaction.
- Manufacturing Giant: A multinational manufacturing firm used OKRs to reduce production downtime and improve safety standards. Their objectives included decreasing machine downtime by 25% and reducing workplace accidents by 50% over the year. Through rigorous process improvements and safety trainings driven by these OKRs, they not only met but exceeded their targets, enhancing productivity and ensuring a safer work environment.
These case studies not only demonstrate the effectiveness of OKRs and KPIs in achieving targeted business outcomes but also underscore their role in driving systemic improvements and fostering an environment of accountability and continuous development.
Future of Goal-Setting and Measurement
Emerging Trends in OKRs and KPIs
The evolution of goal-setting and performance metrics within the modern business landscape is significantly driven by several emerging trends. These trends reflect the integration of advanced technologies and a shift in organizational values towards more dynamic and responsive practices.
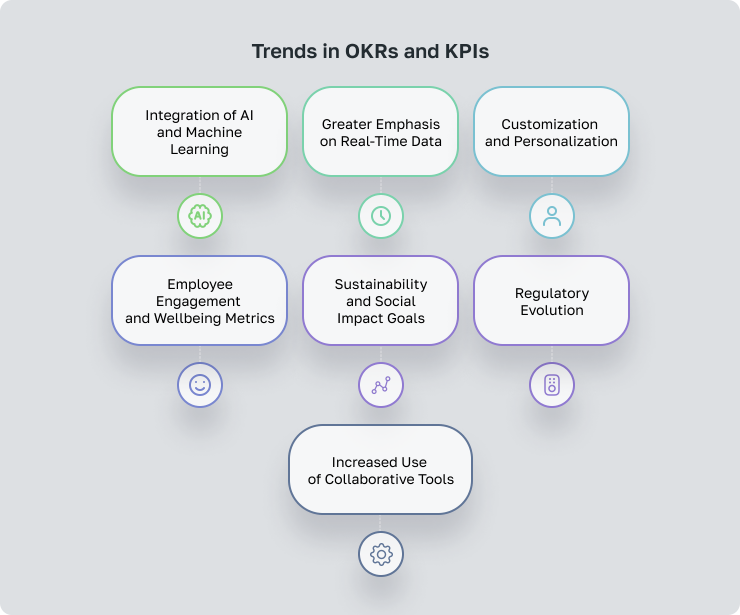
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: More organizations are incorporating AI to refine their OKRs and KPIs, leveraging machine learning algorithms to predict outcomes and analyze performance data more deeply. This technology allows for real-time adjustments in goal-setting processes, ensuring they are based on the most current data, thus enabling companies to achieve optimal results more consistently.
- Greater Emphasis on Real-Time Data: The shift towards real-time data analysis is transforming traditional performance reviews. Businesses are moving away from static, periodic reviews to dynamic, continuous feedback mechanisms. This shift enables quicker responses to market changes and internal dynamics, allowing for timely goal adjustments and fostering a more agile business environment.
- Customization and Personalization: Recognizing the diverse needs of various departments and individual roles, companies are tailoring OKRs and KPIs to better suit specific circumstances. This trend towards customization ensures that the performance measurement tools are relevant and effective, enhancing engagement and efficacy across all levels of the organization.
- Employee Engagement and Wellbeing Metrics: With a growing focus on holistic employee well-being, companies are expanding their metrics to include indicators of employee satisfaction, engagement, mental health, and work-life balance. These metrics are becoming as important as traditional productivity and performance indicators, supporting a more rounded approach to employee assessment.
- Sustainability and Social Impact Goals: There is an increasing drive to integrate sustainability and social responsibility into core business goals. Companies are now setting OKRs and KPIs that not only aim for financial success but also measure impact on environmental sustainability and community welfare. This reflects a broader shift towards ethical business practices that consider long-term societal impacts.
- Regulatory Evolution: As businesses adopt more flexible and globally distributed models, regulatory frameworks are evolving to catch up. This includes clearer guidelines on remote work, data security, and employee rights, which are essential for organizations that leverage a hybrid or fully remote workforce.
- Increased Use of Collaborative Tools: Tools that facilitate collaboration and communication are becoming integral in managing teams that operate under hybrid models. These tools help bridge the gap between different work settings, ensuring that all members of the organization, regardless of location, are aligned and can contribute effectively.
Adapting to Changing Business Landscapes
In dynamic business environments, it’s crucial for organizations to remain agile in their goal-setting and performance measurement approaches. Here’s an expanded view on how businesses can adapt their Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) frameworks to effectively respond to evolving market conditions and organizational needs:- Fostering a Culture of Flexibility and Adaptability: Building a work culture that values adaptability and continuous learning is foundational for resilience. This involves training leaders and teams to integrate flexibility into the goal-setting process, preparing them to handle and embrace changes as they arise.
- Decentralizing Decision-Making: Empowering employees at all levels to set and adjust their own OKRs and KPIs in alignment with overarching business objectives enhances organizational responsiveness. When team members at every level are involved in these processes, it allows for quicker adjustments to goals and strategies, fostering a proactive rather than reactive approach.
- Enhancing Interdepartmental Collaboration: Effective adaptation to changing landscapes often requires breaking down silos within the organization. By utilizing OKRs and KPIs that encourage cross-functional projects and goals, companies can foster collaboration across departments, leading to a more unified and effective response to challenges.
- Leveraging Technology for Scalability: The use of scalable technology is crucial in adapting goal-setting frameworks. Advanced tools that automate data collection and analysis can provide rapid insights into OKRs and KPIs, supporting agile decision-making. These technologies enable organizations to scale up or down with ease and precision.
- Continuous Learning and Development: Investing in continuous training programs ensures that employees are up-to-date with the latest methodologies in OKR and KPI implementation. Regular training sessions help teams better understand and utilize these tools effectively, ensuring that they are aligned with current business strategies and capable of driving meaningful outcomes.
- Iterative Goal Revision: Adopting a mindset of continuous improvement and regular iterations of goal-setting processes can help organizations stay aligned with external and internal shifts. Regularly revisiting and revising OKRs and KPIs ensures that they remain relevant and aligned with the latest business strategies and market conditions.
- Building Resilience Through Feedback: Establishing strong feedback mechanisms where employees can contribute insights and suggestions is crucial for refining OKRs and KPIs. This feedback should be actively sought and utilized to make necessary adjustments, ensuring that the organization’s strategic planning remains on target and effective.
Adopting these strategies will improve your organization’s ability to manage the complexity of the modern business environment and ensure that you are not just surviving, but thriving in the face of change. These practices help maintain a balance between achieving current goals and remaining agile to meet future opportunities and challenges.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
Implementing Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) can significantly enhance strategic management and operational efficiency within an organization.
Here are some crucial insights and best practices gleaned from their application:
- Strategic Alignment: Ensure that both OKRs and KPIs are tightly aligned with the organization’s strategic goals. This alignment helps in focusing efforts on what’s most important, ensuring that all activities contribute directly to the company’s overarching objectives.
- Clarity and Simplicity: Maintain clarity and simplicity in setting OKRs and KPIs. Complex goals can lead to confusion and dilute focus. Clear, concise, and achievable goals ensure that everyone in the organization understands what is expected and how their contributions matter.
- Regular Review and Adjustment: OKRs and KPIs should not be static. Regular reviews (monthly or quarterly) are essential to assess progress and make necessary adjustments. This flexibility allows organizations to respond to changes in the business environment effectively.
- Integration of Technology: Utilize modern technology to track and analyze OKRs and KPIs. Advanced software tools can automate data collection and provide real-time insights, making it easier to monitor progress and make informed decisions quickly.
- Cultural Integration: Embedding OKRs and KPIs into the company culture is vital. They should be part of everyday business processes, with everyone in the organization understanding their importance. This cultural integration helps in fostering a commitment to achieving key results and improving performance continuously.
- Training and Development: Provide ongoing training and support for all employees on how to effectively use OKRs and KPIs. This should include how to set them, track progress, and interpret results. Proper training ensures that these tools are used efficiently and can lead to better outcomes.
- Encouraging Collaboration: OKRs and KPIs should encourage collaboration across departments. Cross-functional goals can help break down silos, foster teamwork, and ensure that different parts of the organization are working harmoniously towards common objectives.
- Transparency and Communication: Maintain transparency in how OKRs and KPIs are set, tracked, and revised. Open communication about these processes ensures that everyone is on the same page and can contribute to discussions about strategic direction and performance improvements.
Organizations can maximize the effectiveness of OKRs and KPIs, drive growth, and ensure sustainable business success by following these best practices.