The opposition of Agile and Waterfall is not as much theoretical as it is practical. The choice of methodology that does not fit your project will, in the best-case scenario, slow down its development or, at worst, will send it to the “Major Fails of the Year” list. Flexible and cascading design of project development (Agile и Waterfall respectively) — is one of the most popular management methodologies.
Having examined your project’s features and having armed yourselves with the knowledge from this article, you will be able to confidently answer the following question: “What will fit my business better — Agile or Waterfall?”
Agile — system of ideas and “flexible” project management principles that serve as a basis for other popular methods, such as Scrum, Kanban, and others. The key principle is the development through short iterations (cycles), and at the end of each of such cycles, the client (user) is getting a working code or product.
Waterfall — project management method that implies sequential order from one stage to another without anything being skipped and with no return to previous stages.
What is Agile
Like other popular project development and management methodologies, Agile emerged comparatively recently in the USA. Unlike CPM and CCPM, a whole group of people, 17 American IT-specialists from the state of Utah, is responsible for the emergence of this flexible development methodology. Along with the “Flexible development of software Manifesto”, where the term “Agile” was first introduced, they came up with 12 principles of Agile-development.
The essence of these principles boils down to the following key principles that define the character of the flexible development method:
- People and collaboration are more important than processes and tools.
- Working product is more important than comprehensive documentation.
- Cooperation with the client is more important than negotiating the contract’s terms.
- Being ready to face changes is more important than following the initial plan.
Agile became the basis for the whole array of flexible methods like Scrum, Lean, and
extreme programming (XP), to name a few.
Scrum — the methodology of flexible development based on Agile, which is based on the “sprint” — a period from 1 to 4 weeks, after which a working version of a product should be obtained.
Lean — method that grew on the basis of Toyota Production System. Its fundamentals are a philosophy of constant improvement at all levels of the organization, where one of the key notions is — value (what the client is ready to pay for).
Extreme Programming (XP) — one of the Agile-methods where an important role is given to the periodic planning game involving the client. It allows to find out all the flaws of the previous integration, tasks priority, and desired product functionality with the client’s wishes taken into consideration.
Advantages and disadvantages of the Agile method
Advantages include:
- Short and clear iterations — development cycles last from 2 weeks to 2 months at the end of which the client gets the working version of a product.
- High degree of executives’, managers’, and clients’ involvement.
- The working product is at the forefront as the main progress indicator — thiscan be viewed both as good and bad since it requires high demands to the selfmanagement.
Waterfall turned out the same way as many other inventions: Herbert Bennington in 1956 and Hosier in 1961 contributed to the development of the methodology while Walker used their work securing the name of the “Waterfall Creator”. As they say, winners are not to bejudged…
Waterfall development model involves the sequential passage of the process, divided into stages. Transition to a new stage is possible only after the completion of the previous one.
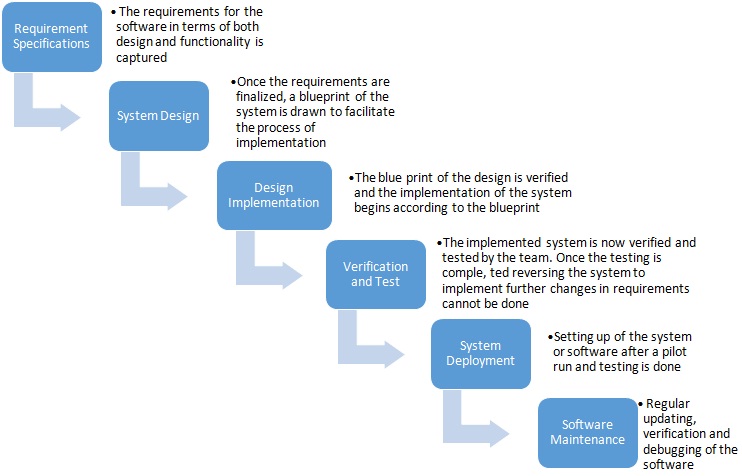
In the original work of Walker “Managing the development of large software systems,” 6 stages of product development are described. These 6 stages were secured in the standards of work with software developers in 1985 by the US Department of Defense:
- System and program requirements: are secured in PRD (product requirements document).
- Analysis: embodied in models, schemes, and business-rules.
- Design: internal software architecture is being developed with ways to implement the requirements. This is not only about the interface and appearance of the software but also about its internal structural logic.
- Coding: program code is written directly; software integration is in progress.
- Testing: Bug testers (testers) check the final product by entering information about defects in the program code or functionality into the trackers. In case of errors and time/money availability, bug fixes occur.
- Operations: the product adapts to different operating systems, is regularly updated to fix bugs found by users and to add functionality. The stage also provides technical support to customers.
The Toyota company that had made the Lean and Kanban methods popular used cascading software developing model till the end of 2000‑s for production needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Waterfall
The biggest advantages of Waterfall are:
- Clear and simple structure of development process — it reduces the entry threshold for teams
- easy reporting — you can easily keep track of resources, risks, time and money spent thanks to the strict phasing of the development process and detailed documentation of the project
- task stability — the tasks that the product faces are clear to the team from the very beginning of development and remain unchanged throughout the entire process
- Estimation of the cost and deadlines for the project — the timing of the finished product as well as its total cost can be calculated before the start of development.
Disadvantages of the cascading method include:
- a process that lacks flexibility – in other words, if a project happens to require more time and financial resources than had been initially allowed, then the whole testing phase goes to shambles. According to research by the Rothman consulting group, the cost of fixing bugs after a product is released is on average 20 times higher than during full-fledged multi-step testing during the development process
- “resistance” to changes — the rigid framework of the development stages and the condition that only the finished product is provided determine that it is impossible to make adjustments during the development
- inertia — in the early stages, the forecast of time and financial expenses may change upwards, but it is impossible to change the project towards optimizing costs and improving the functionality or concept before the release of the finished product
- increased risk — the classic testing system implies testing each component of the project separately (including testing components in cooperation with others). When using Waterfall, the finished product is tested.
Partially the drawbacks of the waterfall development model are corrected in the Waterfall modifications: Sashimi, Waterfall with subprojects, and the waterfall development model with risk-reducing feature.
Waterfall with subprojects is a model in which you work with three large blocks: conceptualization, requirements design, and architectural structure of the product. Then for each of them, you go through the stages (subprojects) of detailed design, coding, and testing. At the end, all components are integrated during the system testing phase.
Waterfall development model with the risk reduction component is a modification of the classic Waterfall, in which risk reduction spirals are added, which divide the project into mini-projects and correspond to one or several key risks.
| Agile | Waterfall | |
|---|---|---|
| Essence | Flexible development model based on iterative principles | Cascading development system based on strict sequential development process |
| Date Created | 2001 | 1956, 1961, and 1970 |
| Application principles |
|
|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
| Clients | Unilever, a number of banks (Alfa Bank, Home Credit, Raiffeisenbank, etc.) | Cisco Ericsson AB, Toyota (till 2010) |
| It will work for you if… |
|
|
| It will not work for you if… |
|
|
Verdict
Agile и Waterfall — two completely different methods of development and project management. Each of them has generated dozens of modifications and methods, “sharpened” for a specific project format.
The flexible model will be ideal for ITcompanies, start-ups, and projects in innovative areas The cascade model does not lose ground in construction projects or projects where the key constraint is the timeframe of the project rather than finance
Taking into consideration the specifics of each of the methods and your business along with risk criteria, time, and involvement of stakeholders, you will be able to independently determine an effective methodology.