Organizational structure of a company helps to see the “inside” of the business: how roles and responsibilities are distributed within it, and even how the main business processes proceed. The business organizational chart helps to identify the “weak points” of the business, effectively plan and reduce costs, and develop a productive management strategy.
In this article, we will talk about the most popular types of organizational structure of an enterprise and figure out how to build an optimal corporate structure chart with org chart examples.
What Is an Organizational Structure?
The organizational structure of an enterprise is a model that explains the relationships between employees or entire departments.
It builds a hierarchy within the company and determines the principle of action when making and executing decisions.
The rights and responsibilities of managers and employees are established based on the organizational structure. In addition, the types of organizational structure influence the key roles to achieve overall business goals.
We will discuss the 10 main organizational structure types common in business management. And let us immediately note: this is not a dogma. There are no restrictions in the selection and application of specific organizational charts. You can adapt the organizational structure for yourself, change or combine different types of organizational systems for different areas of activity. But you need to understand the features of each of the types of organizational structures to do this.
 Hierarchical Organizational structure
Hierarchical Organizational structure
The Hierarchical Organizational structure of a company refers to classic types of organizational systems. It establishes clearly defined functions, rights and responsibilities of employees. The central node is responsible for control.
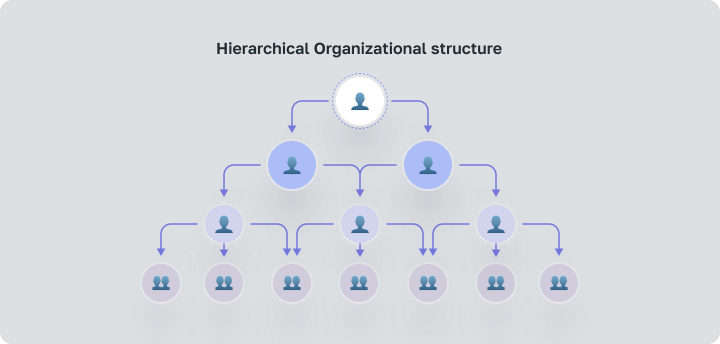
At its core, a hierarchical structure refers to a pyramid: the highest level of power sits at the top, and the levels of power decrease from top to down.
In this method of organization, decision-making is also top-down. Executives or upper management make crucial decisions and then pass them down to middle managers, and further down to lower-level employees for implementation.
There are hierarchical organizations with different levels of management, power or authority. This is the dominant mode for large traditional organizations like Governments and organized religions.
Pros
- Simple and clear organizational structure;
- Has a clear hierarchy and reporting lines;
- Easy to manage;
- Effective for small companies.
Cons
- Inflexible and slow to make decisions;
- Limited communication between departments;
- Not suitable for fast-growing companies.
 Functional Organizational structure
Functional Organizational structure
This type of organizational framework involves the division of responsibilities according to professional skills. Employees are grouped according to the function they provide. Besides the general director, there are directors responsible for their areas: sales, production, marketing director, etc.
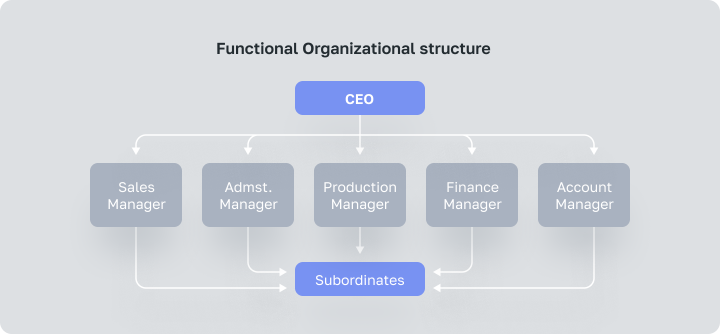
A Functional structure is one of the most common among other types of organizational structures. This structure establishes clear expectations and has a well-defined chain of command. However, this structure runs the risk of being too confining, it can impede employee growth and cross-department communication and collaboration.
At the same time, functional structure facilitates specialization, scalability and accountability. This model is traditionally used by holdings — enterprises with many areas of activity and a wide range of products.
Pros
- High specialization of employees;
- Efficient use of resources;
- Easy to coordinate the work of specialists.
Cons
- Bureaucratic and slow;
- Limited cross-functional communication;
- Not suitable for fast changing markets.
 Horizontal or flat Organizational structure
Horizontal or flat Organizational structure
Management system with a minimum number of middle managers. Decisions in such types of organizational systems are mainly made by line employees with relevant experience and competencies.
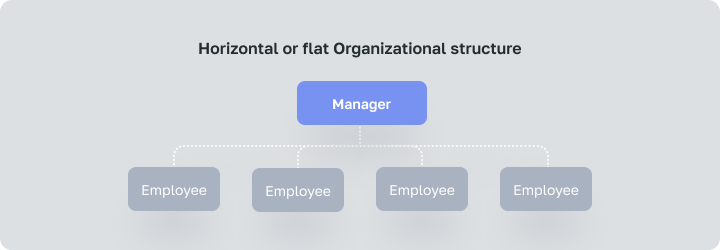
Under a Horizontal structure, the company has a short chain of command. It allows employees to focus and invest time in big goals because they have more autonomy, freedom and independence to carry out their roles and responsibilities.
This corporate structure type is mostly adopted by small companies and start-ups in their early stage because their work and effort in a small company are relatively transparent. So, decision-making power is shared and employees are held accountable for their decisions.
Horizontal or flat Organizational structure is almost impossible or just useless for larger companies with many projects and employees. Most likely, as your business grows, you will have to choose from other types of organizational systems.
Pros
- Fast decision-making;
- Excellent communication and cooperation;
- High employee motivation.
Cons
- Requires highly qualified and self-disciplined employees;
- Not suitable for large companies;
- Complex tasks are difficult to coordinate.
 Divisional Organizational structure
Divisional Organizational structure
In this organizational structure, the general manager is responsible for the strategy and development of the company, and the heads of divisions are responsible for their operational management. The duties, responsibilities and tasks of each manager will depend on the business specific.
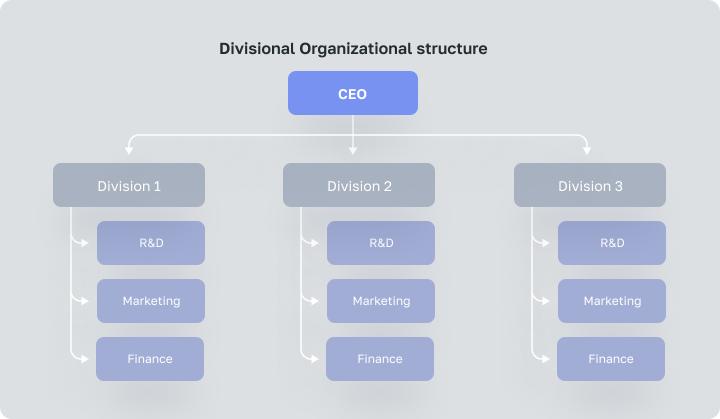
The divisional organizational structure is used more often than other types of organizational systems by corporations and large organizations due to its wider range of products and services. Each division has its own division which corresponds to either products or geographies and contains the necessary resources and functions needed to support the product line and geography.
Such corporations can focus on various divisions more closely with Divisional organizational structure. The main advantage of this structure is the independent operational flow, that failure of one company does not threaten the existence of the others.
Pros
- Quick adaptation to market changes
- Unit autonomy
- Increasing the responsibility of managers.
Cons
- Duplication of functions
- High costs and increase in accounting taxes
- Difficult cross-department coordination.
 Matrix Organizational structure
Matrix Organizational structure
Complex organizational structure, where the performer simultaneously reports to the functional manager and the project manager. Narrow specialists may be temporarily subordinated to the manager of a specific project. However, he is not relieved of his main job.
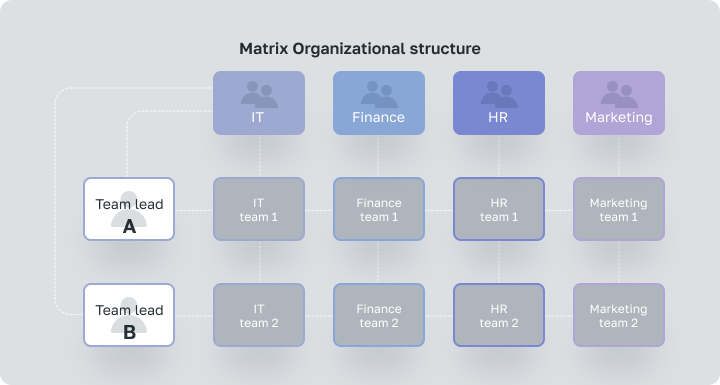
For example, a PR specialist may have reporting obligations within the marketing and product teams. A more complex example for a large company: all engineers may be in one engineering department and report to an engineering manager. But these same engineers may be assigned to different projects and might be reporting to those project managers as well.
A Matrix Organizational structure can be more complex than other types of organizational systems, so it can cause confusion about accountability and communication, especially among new employees. There are multiple reporting obligations in such an organizational structure.
Pros
- Flexible and adaptive organizational structure;
- Efficient use of resources;
- Allows you to implement complex projects.
Cons
- Complex and confusing due to mixing different types of organizational systems
- Requires precise coordination
- May lead to conflicts.
 Team-based Organizational structure
Team-based Organizational structure
Team-based Organizational structure is formed of teams working towards a common goal while working on their individual tasks. Such teams include different specialists (managers, suppliers, production workers, technologists, finance specialists) who work toward a common goal while performing their own specialized tasks.
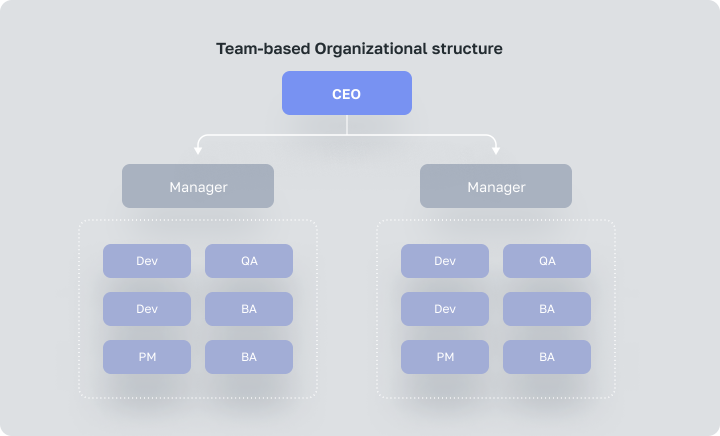
Each team has autonomy and independence and is fully responsible for the results of its work. Because they’re all on the same team and regularly interact with each other, they communicate ideas faster compared with other types of organizational systems. Further, professionals may reach out to other departments within the organization for information.
Team Organization structures have changed the way many industries work around the world to produce goods and services cooperatively. They are less hierarchical and have flexible structures that reinforce problem-solving, decision-making, and teamwork.
Pros
- High employee motivation and involvement;
- Fast decision-making;
- Flexibility and adaptability.
Cons
- Requires compatible teams;
- Not suitable for all tasks;
- It is difficult to coordinate the work of different teams.
 Network Organizational structure
Network Organizational structure
A hybrid solution that combines divisional and matrix types of organizational systems, their adaptability and unified management of basic functions. A network structure prioritizes collaboration and positive relationships more than hierarchy.
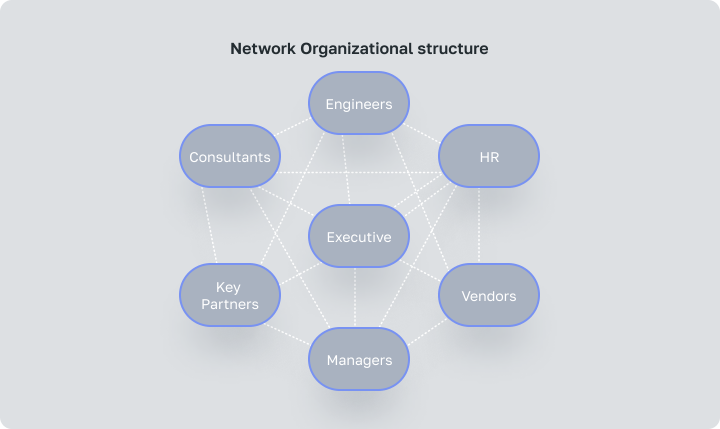
Compared with other types of organizational systems, networked organizations do not have a hierarchical organizational chart. Instead, they make clusters made up of different departments, business units, or local offices, which work together when needed and use the full resources of an organization to meet customer goals.
A Network organizational structure is the most beneficial when a company has many divisional components in different geographic locations. It is a system that involves interacting with internal and external parties to deliver a product or service. By focusing on core competencies, each organization can offer its best products or services to reach defined goals.
Pros
- Flexible and adaptive;
- Low costs;
- Allows to quickly bring new products to market.
Cons
- Complex control;
- Limited coordination;
- Not suitable for all niches.
 Process-based Organizational structure
Process-based Organizational structure
The main feature of the Process-based Organizational structure is the priority of processes rather than functions. For such a company, business is a set of processes, strategic plans, and a sustainable system of improvements. While a strictly functional structure and some other types of organizational systems often compartmentalize work, a process-based approach prioritizes the interconnectedness of tasks within the bigger picture.
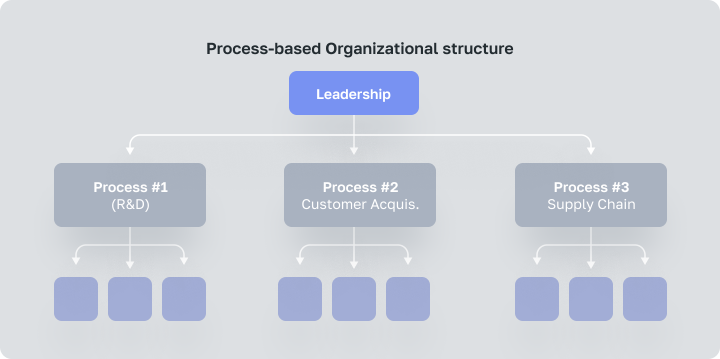
So, the Process-based structure is organized to follow a product’s or service’s life cycle. For example, this organizational structure can be broken down into R&D, product creation, order fulfillment, billing and customer services.
A Process-based organization relies on the idea that final products or services are the result of a sequence of internal processes. All these internal processes should be organized as well as possible. The customer acquisition process can’t start until you have a fully developed product to sell. By the same token, the order fulfillment process can’t start until customers have been acquired and there are product orders to fill.
Customer acquisition and order fulfillment are two sides of the same coin, with one fueling the other in a continuous loop. These processes dance in tandem, where customer acquisition sets the stage, and order fulfillment delivers the performance. Smooth execution requires both processes to be planned and coordinated.
Pros
- Allows to reduce production costs;
- Increases efficiency and speed;
- Each project participant understands the importance of their work.
Cons
- Possible conflicts between the different process groups;
- Could cause communication breakdowns.
 Circular Organizational structure
Circular Organizational structure
Circular Organizational structure is based on a democratic hierarchy. Managers here are not commanders, but leaders. They’re at the center of the organization, spreading their vision outward. Decisions are made collectively by all members of the organization.
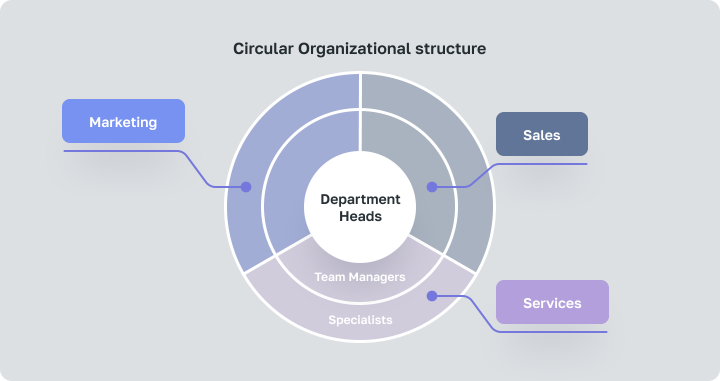
Unlike the siloed nature of traditional types of organizational systems, where departments operate somewhat independently, the circular model visualizes everyone as interconnected parts of a unified whole.
A Circular organization is fostering long-term collaboration and creativity, intending to empower people. Soft skills, such as attitude, teamwork, communication, and decision-making capabilities are critical for a Circular Organizational structure.
Pros
- Information flowing freely across the business;
- Connecting individuals to the bigger picture;
- Encouraging employees to collaborate between departments.
Cons
- Can be confusing, especially for new employees;
- Unclear reporting lines for new hires.
 Line Organizational structure
Line Organizational structure
This is one of the simplest and very common types of organizational systems, consisting of chains, where each level of management has clear authority over the next level down. Decisions go down the chain from the top to the deputies, then to department heads and specialists. The chain of command allows each department head to have control over their departments.
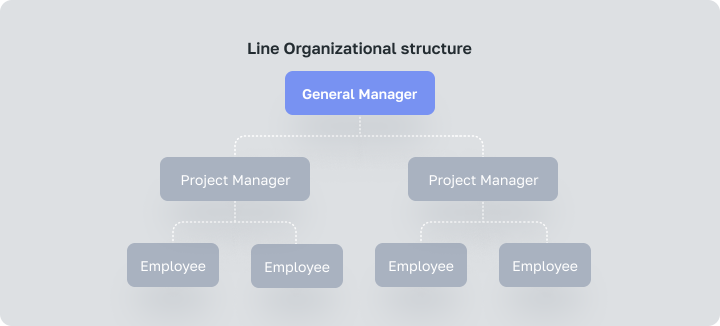
In simple words, line organizations have clear lines of authority (chain of command) running from the top of an organization down to the lowest levels. Independent decisions can be taken by line officers because of its unified structure.
Unlike other structures, supportive services do not take place in these organizations. The main advantage of a line structure can be identified as stability to the company.
Pros
- Simple interaction;
- Rights and responsibilities are clearly delineated;
- High level of discipline and control;
- Performers have opportunities for career growth.
Cons
- Managers deal with a wide range of issues, which can reduce their focus;
- The final decisions of specific individuals, including incorrect ones, affect the entire company;
- There is no communication between performers and higher management levels;
- Opportunities for abuse of power in a high position.
Findings
There are the most common types of organizational structures, but there is no one “right” structure. So, which structure will work best for your company? To find the correct answer, you should know your company very well, from current roles and teams to the strategic plan.
How are job functions currently organized, and does it foster communication and productivity? And what about employee growth? Feedback from employees, leadership and other stakeholders can be very useful in order to find the right approach from many types of organizational formats. But the main goal of the best (for you) organizational structure is to support your strategic plans.
Consider this and don’t doubt about using different flexible and hybrid types of organizational framework. It can change along the life circle and company development. Find your optimal path that will support your productive management strategy.
